Disclaimer:
▪︎This content is Not an official document and does not represent the views of Airbus or any other aviation authority.
▪︎The information provided may be incorrect or misinterpreted and should not be relied upon for decision-making.
▪︎Always refer to official documents and consult with a qualified aviation professional before making any decisions based on the information provided in this blog post.
▪︎The information provided in this blog post is based on personal study and review.
The Influence of V₁ on Accelerate-Go and Accelerate-Stop Distances

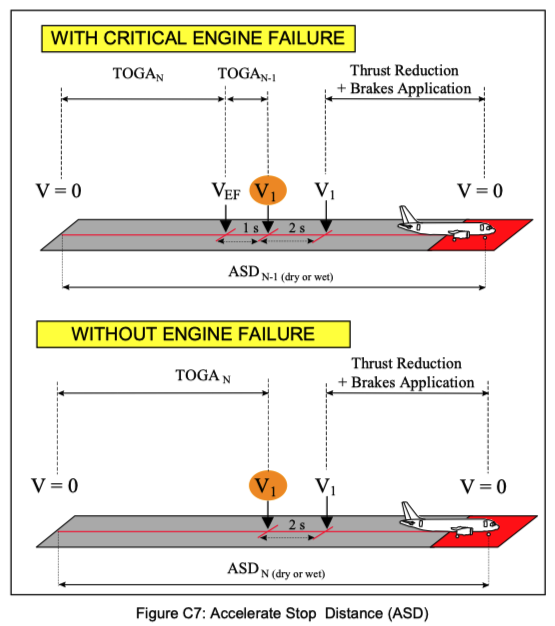
The decision speed, V₁, plays a crucial role in determining both the accelerate-go distance and the accelerate-stop distance during takeoff. It represents the speed at which the pilot must decide whether to continue the takeoff after an engine failure or to abort the takeoff and stop the aircraft.
When V₁ is set higher, an engine failure will occur at a higher speed, meaning the aircraft is already close to rotation speed (VR). As a result, the distance required to continue the takeoff and reach 35 feet of altitude with one engine inoperative becomes shorter, since less additional acceleration is needed. However, if the takeoff is rejected at this higher speed, the aircraft requires more distance to stop because braking from a higher speed takes longer. Therefore, a higher V₁ leads to a shorter accelerate-go distance but a longer accelerate-stop distance.
(beause the pilot will stop the aircraft below V1.)
Conversely, when V₁ is set lower, an engine failure occurs earlier in the takeoff roll. In this case, the aircraft must accelerate farther with only one engine operating to reach VR and climb to 35 feet, which results in a longer accelerate-go distance. On the other hand, if the pilot decides to abort the takeoff, the aircraft will be moving at a lower speed, so it requires less distance to stop. Thus, a lower V₁ produces a longer accelerate-go distance but a shorter accelerate-stop distance.
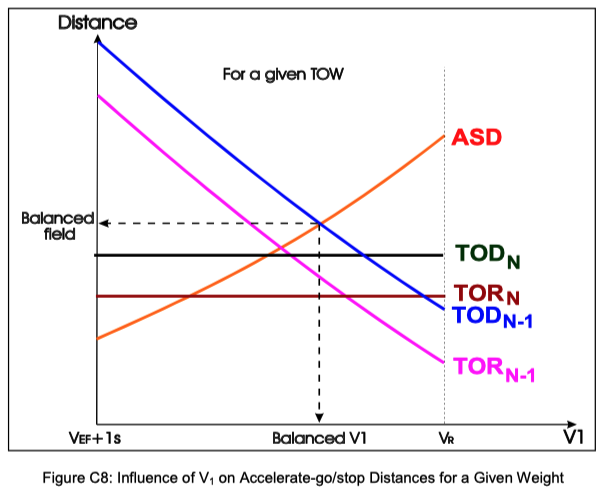
In summary, there is a trade-off between these two distances: as V₁ increases, the accelerate-go distance decreases while the accelerate-stop distance increases, and vice versa. For takeoff performance planning, the required runway length is determined by the greater of the two distances, ensuring that the aircraft can safely either continue or abort the takeoff under any circumstances.
Influence of V₁ on Runway-Limited Takeoff Weight
In practice, every runway has a limited length; there is no such thing as an infinite runway. Therefore, the value of V₁ must be carefully balanced to ensure both accelerate-go and accelerate-stop requirements are met within the available runway distance.
When V₁ is increased, the accelerate-stop distance also increases because the aircraft would be traveling at a higher speed when a rejected takeoff occurs. On a limited runway, this restricts how high V₁ can be set, since the aircraft might not have enough distance to stop safely. Conversely, when V₁ is decreased, the accelerate-go distance increases, as the aircraft must accelerate further on one engine to reach VR and achieve lift-off. This also becomes a limiting factor, because the aircraft may require more runway than what is available.
As a result, V₁ cannot be set arbitrarily high or low. It must remain within a certain balanced range where both the accelerate-stop distance and the accelerate-go distance are equal to or less than the takeoff distance available (TODA). This balance directly affects the runway-limited takeoff weight: if the available runway is short, the maximum allowable takeoff weight must be reduced to ensure that both conditions are satisfied within the runway limits.

Disclaimer:
▪︎This content is Not an official document and does not represent the views of Airbus or any other aviation authority.
▪︎The information provided may be incorrect or misinterpreted and should not be relied upon for decision-making.
▪︎Always refer to official documents and consult with a qualified aviation professional before making any decisions based on the information provided in this blog post.
▪︎The information provided in this blog post is based on personal study and review.
'KNOWLEDGE' 카테고리의 다른 글
| How to Find Official Aeronautical Charts for Vietnam (AIP & Airport Charts) (0) | 2025.08.07 |
|---|---|
| WAKE TURBULENCE SEPARATION (Time based and Distance based) (0) | 2025.07.02 |
| Weather radar and radome. (Cat's Eye) (2) | 2024.09.08 |
| CRM (0) | 2024.05.13 |
| Lost Communication Procedure (1) | 2024.04.19 |



